Guest Post: Rib cage position, breathing and your pelvic floor
I am thrilled today to have my colleague and friend, Seth Oberst, PT, DPT, SCS, CSCS (that's a lot of letters, right?!), guest blogging for me. I have known Seth for a few years, and have consistently been impressed with his expansive knowledge and passion for treating a wide range of patient populations (from men and women with chronic pain, to postpartum moms, and even to high level olympic athletes!) Recently, Seth started working with me at One on One in Vinings/Smyrna, which is super awesome because now we get to collaborate regularly in patient care! Since Seth started with us, we have been co-treating several of my clients with pelvic pain, diastasis rectus, and even post-surgical problems, and Seth has a unique background and skill set which has been extremely valuable to my population (and in all reality, to me too!). If you live in the Atlanta area, I strongly recommend seeing Seth for any orthopedic or chronic pain problems you are having--he rocks! So, I asked Seth to guest blog for us today...and he'll be talking about your diaphragm, rib cage position, and the impact of this on both the pelvis and the rest of the body! I hope you enjoy his post!
~ Jessica
The muscles of the pelvic floor and the diaphragm (our primary muscle of breathing) are mirror images of each other. What one does so does the other. Hodges found that the pelvic floor has both postural and respiratory influences and there’s certainly a relationship between breathing difficulty and pelvic floor dysfunction. (JR note: We've chatted about this before, so if you need a refresher, check out this post) So one of the best ways we can improve pelvic floor dysfunction is improving the way we breathe and the position of our ribcage. Often times, we learn to breathe only in certain mechanical positions and over time and repetition (after all we breathe around 20,000 times per day), this becomes the “normal” breathing posture.
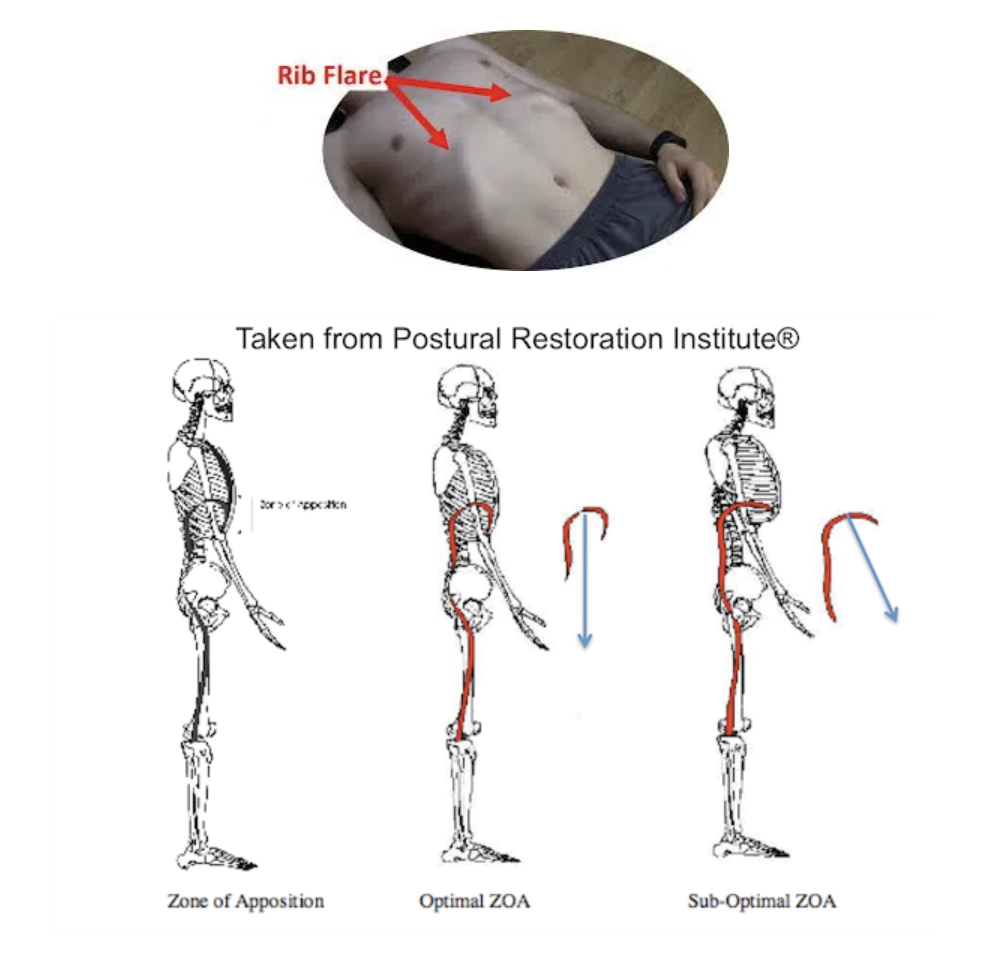
Clinically, the breathing posture I see most commonly is a flared ribcage position in which the ribs are protruding forward. This puts the diaphragm in a position where it cannot adequately descend during inhalation so instead it pulls the ribs forward upon breathing in. The pelvis mirrors this position such that it is tipped forward, causing the muscles of the pelvic floor to increase their tension. (JR note: We see this happen all the time in men and women with pelvic pain!) Normal human behavior involves alternating cycles of on and off, up and down, without thinking about it. However, with stress and injury we lose this harmony causing the ribs to stay flared and the pelvis to stay tilted. Ultimately this disrupts the synchrony of contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and pelvic floor, particularly when there is an asymmetry between the right and left sides (which there often is).
Jessica has written extensively on a myriad of pelvic floor issues (this IS a pelvic health blog, after all) that can be caused by the altered control and position of the rib cage and pelvis that I described above. But, these same altered positions can cause trouble up and down the body. Here are a few ways:
Shoulder problems: The ribcage is the resting place for the scapulae by forming a convex surface for the concave blades. With a flared, overextended spine and ribs the shoulder blades do not sit securely on their foundation. This is a main culprit for scapular winging (something you will often see at the local gym) because the muscles that control the scapulae are not positioned effectively. And a poorly positioned scapula leads to excessive forces on the shoulder joint itself often causing pain when lifting overhead.
Back pain: When stuck in a constant state of extension (ribs flared), muscles of the back and hips are not in a strong position to control the spine subjecting the back to higher than normal forces repeatedly over time. This often begins to manifest with tight, toned-up backs that you can’t seem to loosen with traditional “stretches”.
Hip impingement: With the pelvis tilted forward, the femurs run into the pelvis more easily when squatting, running, etc. By changing the way we control the pelvis (and by association the rib cage), we can create more space for the hip in the socket decreasing the symptoms of hip impingement (pinching, grinding sensation in groin/anterior hip).
Squat Width and Movement Faults
Knee problems: An inability to effectively control the rib cage and pelvis together causes increased shearing forces to the knee joint as evidenced in this study. Furthermore, when we only learn to breathe in certain positions, it reduces our ability to adapt to the environment and move variably increasing our risk for injury.
Foot/ankle: The foot and pelvis share some real estate in the brain and we typically see a connection between foot control and pelvic control. So if the pelvis is stuck in one position and cannot rotate to adapt, the foot/ankle complex is also negatively affected.
So, what can we do about this? One of the most important things we can do is learn to expand the ribcage in all directions instead of just in the front of the chest. This allows better alignment by keeping the ribs down instead of sacrificing position with every breath in. Here are few ideas to help bring the rib cage down over the pelvis and improve expansion. These are by no means complete:
**JR Note: These are great movements, but may not be appropriate for every person, especially if a person has pelvic pain and is at an early stage of treatment (or hasn't been treated yet in physical therapy). For most clients, these exercises are ones that people can be progressed toward, however, make sure to consult with your physical therapist to help determine which movements will be most helpful for you! If you begin a movement, and it feels threatening/harmful to you or causes you to guard your muscles, it may not be the best movement for you at the time.
Crawling Pattern With Exhalation
Respiratory Squat
**JR Note: This squat exercise is very similar to one we use for men and women with pelvic pain to facilitate a better resting state of the pelvic floor. It's wonderful--but it does lead to a maximally lengthened pelvic floor, which can be uncomfortable sometimes for men and women who may have significant tenderness/dysfunction in the pelvic floor (like occurs in men and women with pelvic pain in the earliest stages of treatment).
Quadruped Reach With Breathing
Our ability to maintain a synchronous relationship between the rib cage and pelvis, predominantly thru breathing and postural control, will help regulate the neuromuscular system and ultimately distribute forces throughout the system. And a balanced system is a resilient and efficient one.
Dr. Seth Oberst, DPT is a colleague of Jessica’s at One on One Physical Therapy in Atlanta, GA. He works with a diverse population of clients from those with chronic pain and fatigue to competitive amateur, CrossFit, professional, and Olympic athletes. Dr. Oberst specializes in optimizing movement and behavior to reduce dysfunction and improve resiliency, adaptability, and self-regulation.
For more from Seth check out his Instagram and follow him on Twitter at @SethOberstDPT